জাতীয় দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনা নীতিমালার লক্ষ্য ও উদ্দেশ্য
দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনায় বাংলাদেশ সরকারের লক্ষ্য হলো প্রাকৃতিক, পরিবেশগত ও মনুষ্যসৃষ্ট আপদসমূহের ক্ষেত্রে জনগণের, বিশেষ করে দরিদ্র ও সুবিধা বঞ্চিতদের ঝুঁকি, মানবিক ও গ্রহণযোগ্য পর্যায়ে নামিয়ে আনা এবং বড় মাপের দুর্যোগ মোকাবেলায় সক্ষম ও কার্যকর জরুরি সাড়া প্রদান পদ্ধতি প্রস্তুত রাখা।
জাতীয় দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনা নীতিমালার উদ্দেশ্যসমূহ নিম্নরূপ:
• জ্ঞান, প্রযুক্তি উদ্ভাবন ও শিক্ষার মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ প্রস্তুতি, ঝুঁকিহ্রাস ও সহনশীলতার সংস্কৃতি প্রতিষ্ঠা করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি ব্যবস্থাপনায় জনগণের কার্যকর অংশগ্রহণের কৌশল উদ্ভাবন এবং এর প্রয়োগের মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি পরিকল্পনা প্রণয়নের উদ্যোগ গ্রহণ করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝূঁকিহ্রাস বিষয়ক প্রাতিষ্ঠানিক ও কাঠামোগত সংস্কারের মাধ্যমে কার্যকর দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি ব্যবস্থাপনা প্রতিষ্ঠা করা;
• স্থানীয় প্রেক্ষাপট, সংস্কৃতি ও মূল্যবোধের সাথে সঙ্গতিপূর্ণ দুর্যোগ প্রস্তুতি ও প্রশমনের কার্যক্রম গ্রহণে উৎসাহ প্রদান;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাস কার্যক্রমকে জাতীয় উন্নয়ন পরিকল্পনায় একীভূত করা;
• জনগণের জীবন ও জীবিকায় নিরাপদ খাদ্য সরবরাহের মাধ্যমে খাদ্য নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করে জনগণের বিপদাপন্নতা হ্রাস এবং সরকারি ও বেসরকারি পর্যায়ে দুর্যোগ ঝূঁকিহ্রাস কার্যক্রম গ্রহণে উদ্বুদ্ধ করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাস কার্যক্রমে সরকারি ও বেসরকারি অংশীদারিত্ব প্রতিষ্ঠা ও সুশাসন প্রতিষ্ঠার মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি ব্যবস্থাপনার কার্যকর কৌশল উদ্ভাবন করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাস কার্যক্রমে গণমাধ্যমের অংশগ্রহণ নিশ্চিত করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি ব্যবস্থাপনা কার্যক্রমে স্থানীয় জ্ঞান ও প্রযুক্তির ব্যবহার, স্বল্পব্যয়ী অথচ টেকসই পদ্ধতিসমূহ বাস্তবায়নে উৎসাহিত করা;
• আধুনিক ও কার্যকর দুর্যোগ সতর্ক সংকেত উদ্ভাবন ও প্রত্যন্ত অঞ্চলে সম্প্রচারের কৌশল উদ্ভাবনে বিশেষ প্রচেষ্টা গ্রহণ;
• দুর্যোগ ঝূঁকিহ্রাস কার্যক্রমে স্থানীয় সরকার প্রতিষ্ঠানসমূহকে সম্পৃক্ত করে এর ক্ষমতায়ন ও সাড়াদানের সক্ষমতা বৃদ্ধি করা;
• দক্ষ ও দ্রুত সাড়াদান কর্মকৌশল উদ্ভাবন ও বাস্তবায়ন করা;
• সাড়াদান কার্যক্রম বাস্তবায়নের লক্ষ্যে দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনার অংশ হিসেবে সমাজ ভিত্তিক দুর্যোগ স্বেচ্ছাসেবক সংগঠন গড়ে তোলা এবং সারা দেশব্যাপী সম্প্রসারণ
(T) খাতভিত্তিক চাহিদা ও ক্ষয়ক্ষতি নিরূপণের পদ্ধতি আন্তর্জাতিক মানসম্পন্ন করা; খাত ভিত্তিক দুর্যোগ পরবর্তী সমন্বিত পুনরুদ্ধার এবং পুনর্গঠন প্রক্রিয়া নিশ্চিত করা; দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনার অংশ হিসাবে জাতীয় দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনা প্লাটফরম প্রতিষ্ঠা ও কার্যকর করা; উন্নয়ন পরিকল্পনা ও বাজেট প্রক্রিয়ায় দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাসকে প্রাধান্য দেয়া;
• দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনা নিয়ন্ত্রক কাঠামো বাস্তবায়নের মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনায় পেশাদারিত্ব আনয়ন;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাস ও জলবায়ু পরিবর্তন অভিযোজনকে মূলধারায়নের মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনা কাঠামোর সক্ষমতা বৃদ্ধি করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকিহ্রাস ও জলবায়ু পরিবর্তন অভিযোজন নিশ্চিত করার মাধ্যমে প্রাতিষ্ঠানিক সক্ষমতা বৃদ্ধি করা;
• দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনার ক্ষেত্রে দুর্যোগ প্রতিরোধ, প্রশমন, প্রস্তুতি, সাড়াদান, পুনরুদ্ধার এবং পুনর্বাসনকে প্রেক্ষিত বিবেচনায় সমগুরুত্ব প্রদান করা। এক্ষেত্রে অপেক্ষাকৃত দীর্ঘমেয়াদী পুনর্বাসনের কাজে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ঘাটতি পুরণের লক্ষ্যে দ্রুত পুনরুদ্ধার (Early Recovery) কার্যক্রম পরিচালনা করা;
• নগর জনসংখ্যা বৃদ্ধির প্রেক্ষাপটে নগর ঝুঁকি ব্যবস্থাপনায় অধিকতর গুরুত্ব প্রদান করা;
• অধিকতর ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ এবং বিপদাপন্ন দুর্যোগপ্রবণ এলাকা এবং প্রতিবেশ বিপন্ন (Ecologically Fragile) এলাকাকে প্রাধান্য দিয়ে দুর্যোগ ব্যবস্থাপনার কার্যক্রম নেওয়া। এ বিষয়ে ঝুঁকি ও বিপদাপন্নতার বিশ্লেষণ একটি নিয়ত প্রক্রিয়া হিসেবে বিবেচনা করা;
• দুর্যোগ ঝুঁকি নিরূপণে স্থানীয় জনগোষ্ঠীকে সম্পৃক্ত করার মাধ্যমে ক্ষমতায়ন নিশ্চিত করা;
• সামাজিক নিরাপত্তা কার্যক্রমের মাধ্যমে স্থানীয় জনগোষ্ঠীর বিপদাপন্নতা হ্রাস করা ও জাতীয় খাদ্য নিরাপত্তা পদ্ধতি জোরদার করা;
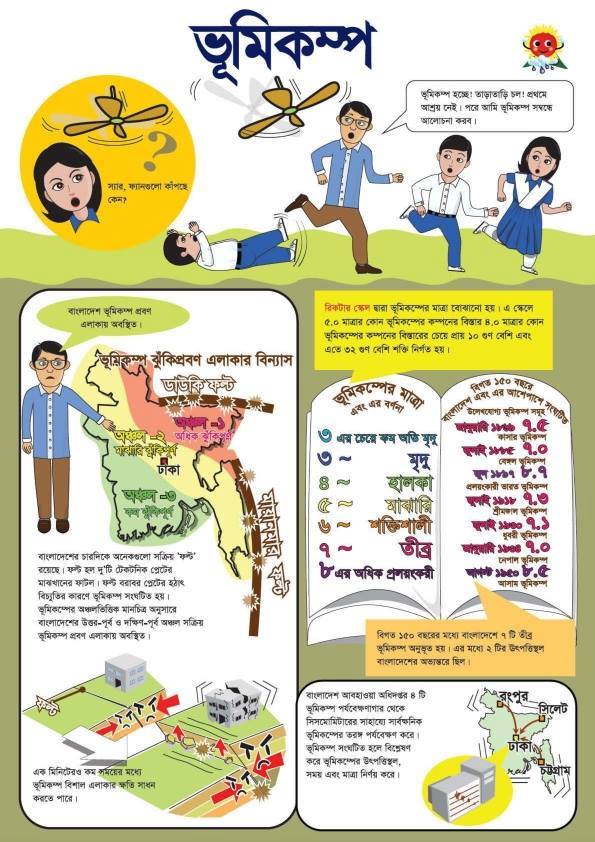
• ভূমিকম্প ঝুঁকি নিরূপণ এবং মাইক্রোজোনেশন ম্যাপিং এর মাধ্যমে দুর্যোগ মোকাবেলার প্রস্তুতি গ্রহণ করা;
• আপদভিত্তিক সতর্ক সংকেত প্রণয়ন ও প্রতিষ্ঠা করা এবং রিয়েল টাইম তথ্য আদান প্রদানের মাধ্যমে আঞ্চলিক নেটওয়ার্ক প্রতিষ্ঠা করা;
• অনুসন্ধান ও উদ্ধার তৎপরতা প্রতিষ্ঠা ও উন্নয়ন করা, স্বেচ্ছাসেবক দল গঠন, কার্যকর Incident Management System (IMS) প্রতিষ্ঠা করা;
Strategic Goals:- To achieve a paradigm shift towards a comprehensive disaster risk reduction some of the strategic goals are as below:-
-Professionalizing the disaster management system
-Mainstreaming risk reduction
-Strengthening institutional mechanism
-Empowering at risk community
-Expanding risk reduction program
-Strengthening emergency response system
-Developing and strengthening networks.
Targets for the future five year plan:
• Upgrade the disaster management regulative framework
• Risk reduction and climate change adaptation principles (with sustainability) are mainstreamed within all development programs, plans and policies
• Create a national training capacity to sustain and progressively expand the training efforts
• Strengthen community and household level capacity to withstand the disastrous situation
• Establishment of DM fund
• Implementation of different risk reduction options
• Spatial Difference Basis Sustainable livelihood Strategy
• Develop, establish & amend emergency response plan
• Establishment of Multi Risk Vulnerability Assessment Mapping(MRVA) & Damage & Need Assessment Cell(DNA)
• Construction of Flood, Cyclone Shelters and killa
• Procuring search & rescue equipments
• Strengthen national capacity for response management support to local disaster management committees
• ICT based Multi-hazard EWS at community level
• Establish and improve search and rescue mechanism
• Develop and establish emergency response plan
• Development of an effective ICT based information management system
• Establish public private partnership for disaster risk reduction
• Establish Go- NGO and private sector coordination for disaster risk reduction
• Establish multi sectoral coordination system
• Reduce vulnerability of the at risk communities through social safety nets
• Prepare guideline for damage & needs assessment for recovery planning
• Establish & strengthen the regional networks
• Strengthen the use of space based technology
• Develop a monitoring and evaluation system to enable the effectiveness of the capacity building strategy to be measured
. Current and future Challenges
There is an estimate that climate change would bear some 75 to 80 percent of the costs of damages caused by the changing climate. Bangladesh lacks sufficient financial and technical capacities to manage increasing climate risk. We depend more directly on climate-sensitive natural resources for income and wellbeing. An equitable and effective global climate deal is needed. Such a deal would recognize the varying needs and constraints and assist with the finance and technology to meet the increased challenges to development, ensure that we are not locked into a permanently low share of the global commons and establish mechanisms that decouple where mitigation happens from who pays for it.
More than 60 % of urban population lives in four main cities in Bangladesh. Dhaka alone accommodates one-third of urban population and produces 60 % of national GDP. Therefore, disaster in urban areas has severe national consequences in Bangladesh. Eventually, disaster risk reduction from the cities should be the key issues for ensuring overall development of Bangladesh.
Today, most of the people in the south say, they are affected by salinity. Farmers are adapting by planting saline-tolerant varieties of rice. But this worked well, until the cyclone Aila hit the country in 2009. After that the salinity level rose higher and even the new crops . It is estimated that for just four villages in the district, the cyclone resulted in a loss of US$1.9 million between 2009-2011.In order to effectively address loss and damage, the following steps may be undertaken:
a. Develop a comprehensive policy on the integration of DRR and CCA to address loss and damage from the impacts of both extreme events and slow onset processes;
b. Establish a policy body under the Ministry of Planning (MoP) and technical bodies at both the MoEF and the MoDMR, to serve as knowledge hubs and to provide expertise in DRR and CCA respectively to the loss and damage policy wing of the MoP; Establishing Links between Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation in the Context of Loss and Damage
c. Integrate DRR and CCA in a multi-level institutional framework to address loss and damage from both extreme events and slow onset processes under a common mechanism;
d. Strengthen and enhance the capacity for mainstreaming loss and damage into national planning processes and develop vertical and horizontal linkages between sectors and institutions working in areas of development to ensure climate resilient development; and
e. Obtain accreditation for the existing National Funding Entities to become National Implementing Entities in order to access support from the international funding mechanisms–both within and outside the UNFCCC – to address loss and damage including through adaptation, mitigation, technology and capacity building.
f. Information is especially important in the case of Trans-boundary water management. Moreover, in Trans-boundary basins, information exchange and sharing of data between riparian countries is regarded as a first and essential step towards fostering cooperation and trust. Unfortunately, restriction in the availability of data and information beyond borders in the riparian countries of the Ganges basin continue to prevail, and countries are often hesitant and cautious to share any kind of hydrological information.
g. Establishing public-private partnerships for disaster & climate change risk reduction.
Sectoral/sub sectoral development strategies and policies for
- Institutionalization of DRR and CCA
- Promoting and practicing Public Private partnership
- Adaptive research on disaster and climatic issues
- Promote proven technologies
. List of policies/ programs/projects for achieving the target
- DM Act 2012
- National Plan for Disaster Management (2010- 2015)
- DM Act derivative rules
- SOD
- Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) 2005-2015
- SAARC Framework for Action (SFA) 2006-2015
- SDGs
- Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan
- National adaptation Plan of Action (NAPA)
- Disaster Management Regulatory Frameworks
- Disaster Management Plan for District Upazila, Union, City corporation, Municipality etc.
- Different sectoral development plan
- Disaster Impact and Risk Assessment Guideline
- Local Disaster Risk Reduction Fund Management Guidelines
- Emergency Fund Management Guidelines
- Indigenous Coping Mechanism Guidebook
- Community Risk Assessment Guidelines
- Damage and Needs Assessment Methodology
- Hazard Specific Risk Assessment Guidelines
- Emergency Response and Information Management Guideline
- National Risk Reduction Fund Management Guideline
- National Disaster Reduction and Emergency Fund Management Guideline
- Local Disaster Management Fund Guideline
- Guideline for Road and Water Safety
- Guideline for Industrial Safety
- Guideline for Disaster Shelter Management
- Monitoring and Evaluation Guideline for the Implementation of the Plan
- Guideline for International Assistance in Disaster Emergency
7. Institutional Mechanism for Monitoring
a. Developing a vulnerability Index will help channelize equitable resources to the targeted districts.
b. Developing focused and specific DRR-CCA indicators in the overall performance tracking for the plans, programs and projects
c. Number of recipients of social welfare/safety net allocations after any disaster.
8. Improving Implementation Capacity
a. Business process and financial management reform in MoDMR and DDM and relevant GoB agencies
b. Better coordination mechanisms within the ministry and across the government
c. Investment in DRR and climate risk reduction to reduce the cost for response and recovery.